
- September 11, 2025
- TechnoVera
- 0
Space exploration has always pushed the boundaries of human knowledge, innovation, and technology. From landing on the Moon to exploring Mars, every milestone in space science has been fuelled by ground-breaking tools. Now, the next big leap is here—artificial intelligence (AI) in space exploration.
AI is not just helping scientists analyze vast amounts of cosmic data; it is also powering autonomous spacecraft, guiding rovers on distant planets, and even predicting space weather. The question is no longer whether AI belongs in space technology—it is how far AI can take us into the unknown universe.
In this blog, we’ll explore how artificial intelligence is transforming space exploration, its advantages and challenges, and what the future of AI in astronomy and space research looks like.
Exploring space presents challenges far beyond human capacity. Missions require fast decision-making, real-time analysis, and self-learning systems because delays in communication between Earth and deep space can be critical. For example, a signal to Mars can take up to 20 minutes to reach, making real-time human control impossible.
This is where AI in space technology becomes a game-changer:
- Autonomous decision-making: AI enables spacecraft and rovers to make decisions without waiting for human input.
- Big data processing: Telescopes and satellites generate enormous data. AI helps filter, classify, and analyze this information quickly.
- Predictive modelling: AI predicts potential risks like system failures, space weather, or asteroid paths.
- Cost efficiency: AI reduces human dependency, saving costs in training, crewed missions, and operations.
Key Applications of AI in Space Exploration
1. AI-Powered Spacecraft and Rovers
NASA and other space agencies use AI-powered rovers like Curiosity and Perseverance on Mars. These rovers use AI to navigate rough terrain, avoid obstacles, and decide the best route—all without direct human intervention.
Future AI spacecraft could explore distant planets and moons, making autonomous decisions to adapt to unknown environments.
2. AI in Astronomy and Data Analysis

Modern telescopes such as the James Webb Space Telescope and other observatories produce terabytes of data daily. AI algorithms help astronomers discover new planets, galaxies, and cosmic phenomena by recognizing patterns humans might miss.
For example, AI has already assisted in identifying exoplanets and even detecting signals that could indicate habitable worlds.
3. Space Debris Management with AI
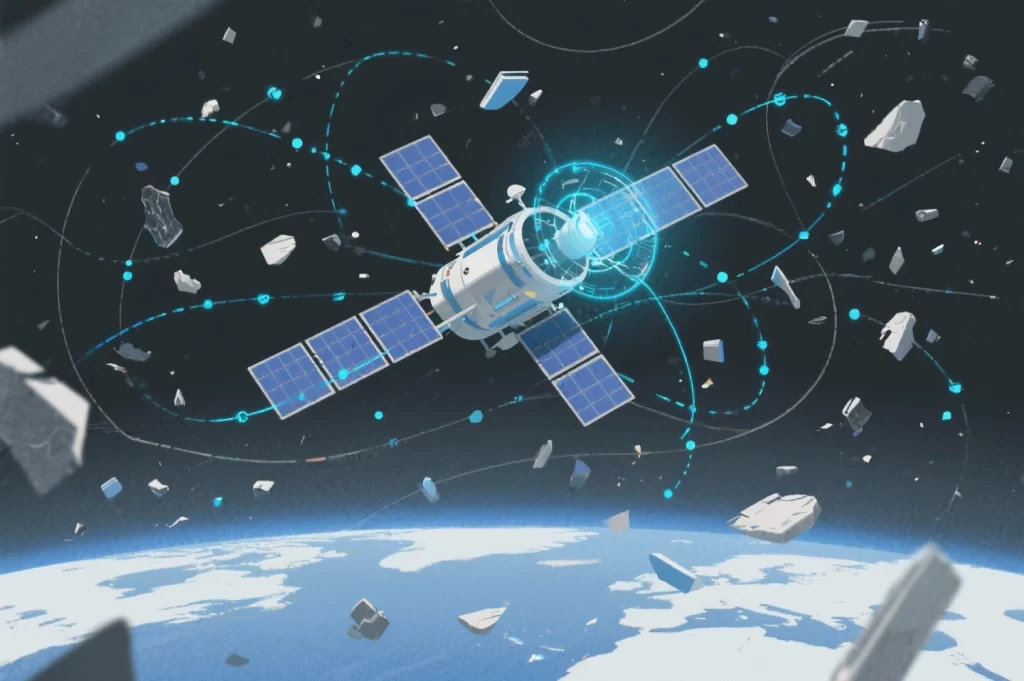

One of the biggest threats to satellites and future space missions is space debris. AI is now being used to track orbital junk, predict collisions, and design autonomous systems that could remove dangerous debris from Earth’s orbit.
This role of AI is vital for sustainable space exploration.
On long-duration missions, astronauts face physical and mental challenges. AI systems like CIMON (Crew Interactive Mobile Companion), used on the International Space Station, act as intelligent assistants. They help astronauts with research tasks, problem-solving, and even conversation to reduce stress during isolation.
AI enables smart satellite systems that optimize bandwidth, predict technical issues, and manage communication networks more effectively. This is particularly useful for Earth observation and global internet connectivity projects.
The integration of artificial intelligence in space exploration comes with significant advantages:
- Autonomy in Deep Space Missions – AI allows spacecraft to operate independently in environments where real-time human guidance is impossible.
- Enhanced Safety – AI predicts equipment failures, protecting astronauts and spacecraft from disasters.
- Cost-Effective Operations – Reduces dependency on large ground teams and lowers mission costs.
- Efficient Data Handling – AI can analyze and classify astronomical data faster than traditional methods.
- Extended Mission Life – By continuously learning and adapting, AI extends the functionality and lifespan of space missions.
Challenges and Disadvantages of AI in Space
While AI offers countless opportunities, it also comes with challenges and risks:
- Cybersecurity Risks – AI systems in satellites and spacecraft could be vulnerable to hacking.
- Technical Failures – If an AI algorithm fails mid-mission, recovery could be impossible without human oversight.
- Ethical Concerns – Relying too much on AI raises ethical questions about control and accountability in space exploration.
- High Development Costs – Designing reliable AI for space is expensive and requires years of research.
- Limited Adaptability – While AI can learn, it still struggles with entirely new, unpredictable cosmic events.
Future of AI in Space Exploration
The future of space exploration with AI is promising and full of possibilities:
- Autonomous Space Colonies: AI could manage life-support systems, resource distribution, and maintenance on Mars or the Moon.
- AI-Powered Deep Space Missions: Future probes could explore distant galaxies with complete autonomy.
- Smarter Space Telescopes: AI could help telescopes detect faint signals of extra-terrestrial life.
- AI and Space Mining: Robots powered by AI might extract minerals from asteroids to support Earth and space colonies.
- Collaboration Between AI and Humans: Instead of replacing astronauts, AI will act as their intelligent partner, ensuring safer and more successful missions.
Conclusion:
Artificial intelligence is no longer just an assistant; it is becoming a driving force in space exploration. From guiding rovers on Mars to analyzing cosmic data, predicting space debris risks, and supporting astronauts, AI in space technology is rewriting the future of aeronautics and astronomy.
The journey ahead is not about AI replacing humans but about AI and humans working together to unlock the mysteries of the universe. As we look toward colonizing Mars, mining asteroids, and exploring beyond our solar system, AI will be the ultimate co-pilot of humanity’s greatest adventure.
